Gigabit broadband: what does it mean for consumers and society?
Imagine a world where you could have remote access to a healthcare specialist who could assess, diagnose and potentially treat you at home; or a school lesson where you’re virtually ‘transported’ to the surface of the moon to learn about the solar system; or a meeting with colleagues who are in different parts of the world which, unlike the one-dimensional video conference calls of today, provides the physical and emotional sensation of literally being in the same room as you. The technological building blocks—such as sensors, screens and processors—are ready or in development. These experiences are also dependent upon high capacity networks. Liberty Global is making this a reality, having made gigabit services available across its European footprint.
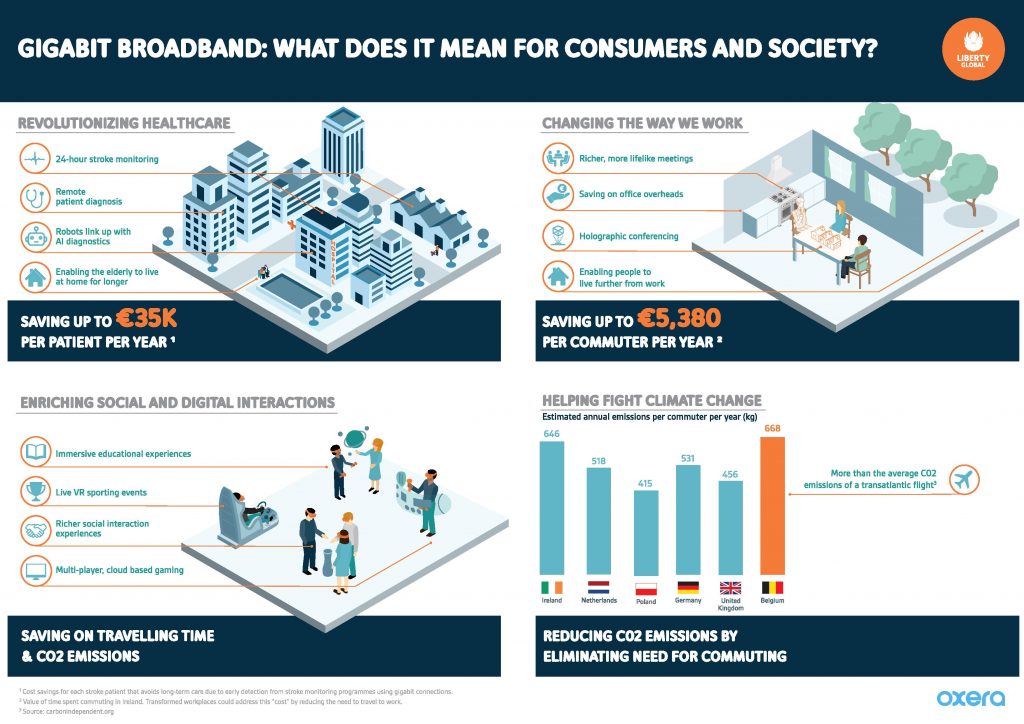
Digital services have already brought significant benefits to society in terms of wellbeing, convenience and user experiences. More of these could be unlocked as a result of the widespread roll-out of gigabit broadband, GigaCities as Liberty Global calls them, which are likely to allow a new generation of digital services to tackle some of the challenges faced in society today. This is a continuation of a trend that began over a century ago, which has seen the evolution of communications technology dramatically change the way we interact with each other by reducing frictions, or what economists call ‘transaction costs’. Reducing these costs lowers barriers to interacting and transacting with one another, facilitating easier and happier lives.
Previous improvements in connectivity have led to significant benefits in terms of communication, sharing and reducing barriers to trade. Gigabit connections could continue this trend by reducing the significant frictions that remain—particularly in the areas of healthcare, commuting, social interaction and the environment.
Gigabit speeds and the accompanying fall in latency (a measure of the time taken for data to cross the network), could enable consumers to use a range of technologies – such as cloud-based gaming, digital health and virtual and augmented reality – in new ways. These changes are likely to be transformative rather than marginal.
This report identifies four key areas in which the mass-market roll-out of gigabit broadband has the potential to transform lives—by eliminating some of the ‘frictions’ that remain.

